Alt-R™ Genome Editing Detection Kit
For detection of on-target or known off-target CRISPR events in cultured cells.
Ordering
The T7 endonuclease I (T7EI) mismatch cleavage assay detects on-target genome editing and estimates genome editing efficiency in CRISPR-treated cells.
- Straightforward—use standard molecular biology techniques
- Fast—does not require purification of PCR products before analysis
- Consistent—analyze easy-to-read electrophoresis results
- Quantifiable—gel band intensities relate to genome editing efficiency
- Versatile—convenient for a single sample or high throughput analysis in plate format
Use the control primer mixes below with the Alt-R Genome Editing Detection Kit to determine editing efficiency in samples transfected with Alt-R CRISPR HPRT Positive Control crRNAs [available for the Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 System and Alt-R CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) System].
Product Details
How the T7EI assay works
- Amplify the targeted genomic region with PCR.
- Denature and reanneal PCR products in a thermal cycler to allow potential heteroduplex formation between wild-type and CRISPR–mutated DNA.
- Digest reannealed PCR products with T7EI, which cleaves mismatched DNA heteroduplexes.
- Analyze results using gel or capillary electrophoresis.
Tips for PCR design for the T7EI assay
Design PCR primers that amplify your experimental target site and adjacent sequences. We recommend using PCR amplicons that are 600–1000 bp in length with at least 100 bp flanking each side of the CRISPR cut site. Position the CRISPR cut site off-center to allow for 2 distinctive digestion product sizes on the gel. Carefully optimize PCR conditions and confirm by electrophoresis that a single PCR product is amplified from genomic DNA prior to editing. For PCR design assistance, use the PrimerQuest™ Tool at www.idtdna.com/PrimerQuest.
For both the Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 System and the Alt-R CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) System, we offer recommended products and sequences for guide RNA positive controls that target HPRT in human, mouse, and rat cells. We have also designed and tested companion PCR primers for use with the Alt-R Genome Editing Detection Kit, which can be used to analyze editing efficiency in the positive control samples.
Product Data
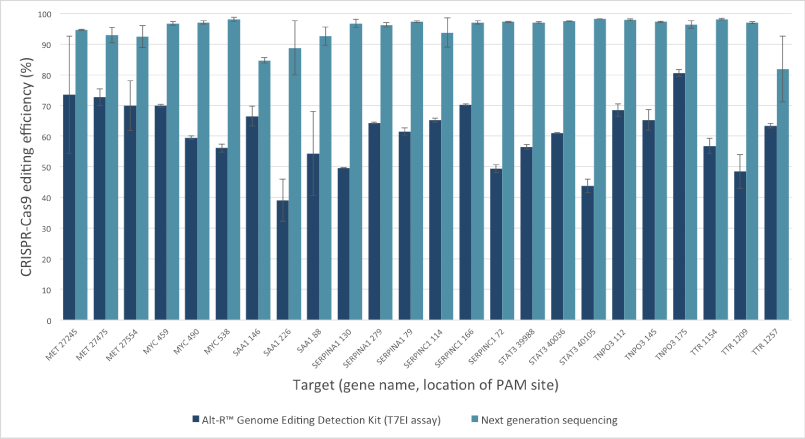
Mutation detection in CRISPR experiments: Comparison of the Alt-R Genome Editing Detection Kit to targeted next generation sequencing
The Alt-R Genome Editing Detection Kit, a T7EI mismatch endonuclease assay, provides a good estimate of genome editing efficiency. However, because T7EI endonuclease does not recognize single-base insertions or deletions, this method underestimates editing efficiency when compared to next generation sequencing (NGS). The amount of underestimation by the T7EI assay varies by target and is dependent on the non‑homologous end joining (NHEJ)‑mediated repair events that follow Cas9 cleavage.
Figure 2. T7EI mismatch endonuclease assays provide a good estimate of genome editing efficiency, but underestimate efficiency when compared to next generation sequencing (NGS) results. The Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 RNA oligonucleotides (30 nM) were introduced by lipofection into HEK-293 cells that stably express Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9. 3 PAM sites were targeted in each of 8 genes. To estimate editing efficiency, genomic DNA samples from the transfected cells were tested using the Alt-R Genome Editing Detection Kit (dark blue bars), which provides reagents needed to run T7EI assays. The same DNA samples were also analyzed using targeted NGS (light blue bars). Amplicons were run an MiSeq® system (Illumina) and data were analyzed using a publicly available data processing program. Error bars represent standard deviation for triplicate lipofection experiments (technical replicates). (n = 1 per gene target location)
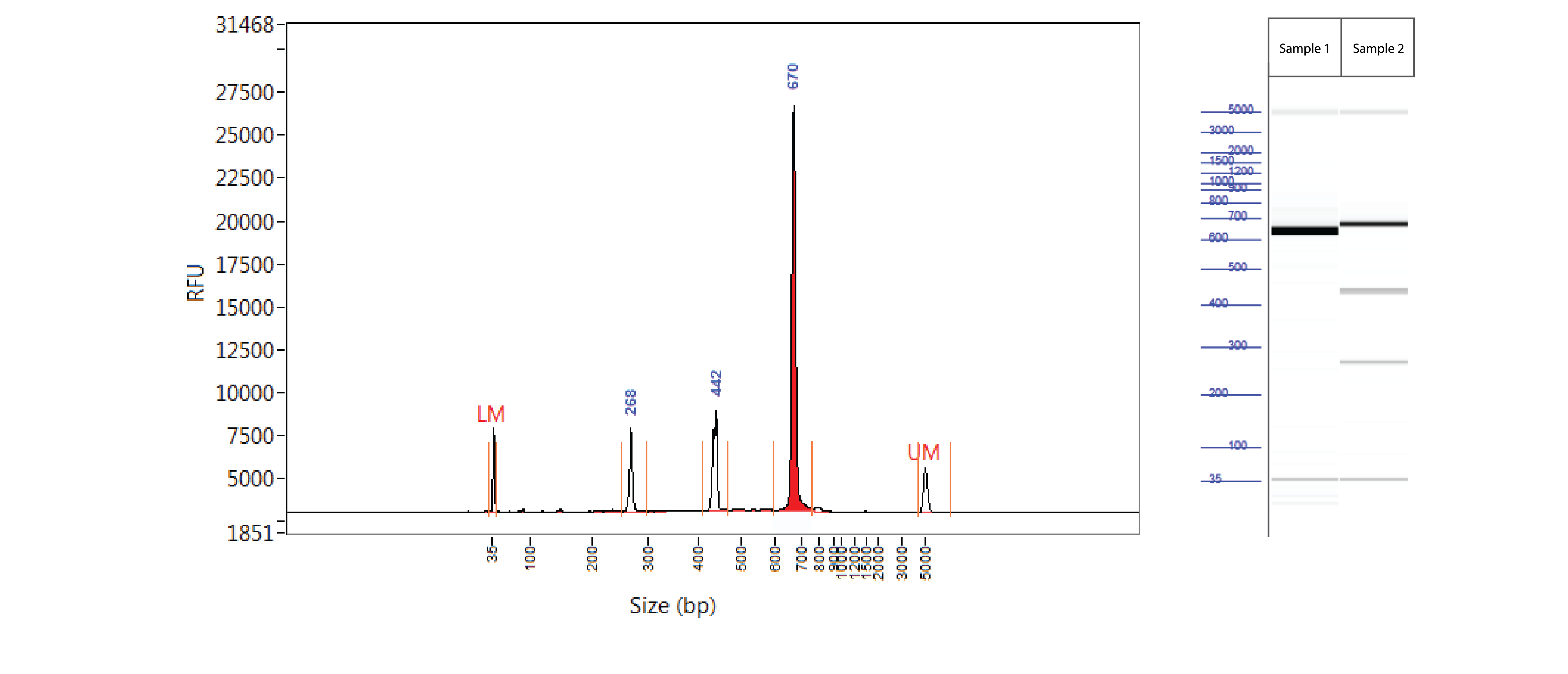
Positive control: T7EI mutation cleavage assay
Controls A and B from the Alt-R Genome Editing Detection Kit provide a robust control for the T7EI assay to show that the assay is functioning. Full-length PCR fragments for Controls A and B are 692 and 686 bp, respectively. T7EI digestion products are approximately 436 and 256 bp.
Figure 3. Easy-to-read results from T7EI mutation cleavage assay analyzed on a Fragment Analyzer™ system. PCR using template and primers in Controls A and B (Alt-R Genome Editing Detection Kit) were run using KAPA HiFi HotStart DNA Polymerase (Kapa Biosystems). Cycling conditions were 5 min. 95°C; 30 x (20 sec. 98°C, 15 sec. 64°C, 30 sec. 72°C); 2 min. 72°C. PCR products were denatured and reannealed in a thermal cycler (10 min. 95°C; 95–85°C (ramp rate of –2°C/sec); 85–25°C (ramp rate of –0.3°C/sec). Sample 1 contains Control A PCR products, while Sample 2 contains homoduplexes and heteroduplexes of Control A and B PCR products. Reannealed PCR products were digested with 2 U of T7EI for 60 min at 37°C. Digestion reactions were analyzed on a Fragment Analyzer system (Advanced Analytical Technologies, Inc.). Trace (left) shows results from Sample 2. Gel image (right) shows results for Samples 1 and 2. LM = lower marker; UM = upper marker (n = 1).
Positive control: CRISPR editing (human, mouse, or rat HPRT)
The results from positive control experiments are important for research publications and provide useful information, should you need to troubleshoot your experiments.
Confirm that your CRISPR editing conditions are working by using Alt-R HPRT Positive Control guide RNAs (human, mouse, or rat). We offer distinct, positive control guide RNAs for the Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 and Alt-R CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) Systems.
To track genome editing in your positive control samples, use the Alt-R Genome Editing Detection Kit and CRISPR Control Primer Mixes (human, mouse, or rat). The control PCR primers are designed to work with either Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 or Alt-R CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) Systems.
Figure 4. Sample data from T7EI digestion of Alt-R CRISPR HPRT Positive Controls. Genomic DNA from CRISPR-Cas9 (A) and CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) (B) edited human, mouse, and rat HPRT controls were PCR amplified, digested using T7 endonuclease I, and run on the Fragment Analyzer system (Advanced Analytical Technologies, Inc.). Reference standard bands at 5000 bp (upper marker) and 35 bp (lower marker) are used to align the gel and analyze the results. Estimated band sizes for the cut and uncut positive control amplicons are listed in the tables. Cell lines used were HEK-293 (human), Hepa1-6 (mouse), and RG2 (rat). The PCR annealing temperature for human and mouse primers is 67°C, and for rat primers is 64°C (n = 1).
Negative control: CRISPR genome editing
Amplification of the negative control wells with your experimental primers and cycling conditions should result in only full-length products in the T7EI assay.
Using Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 Negative Control crRNA #1, #2, or #3 in your editing experiments will support a conclusion that cleavage products from the T7EI assay result from target-specific recognition and cleavage by Cas9, and not other factors associated with transfection or electroporation. Note: Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 Negative Control crRNAs #1, #2, and #3 are computationally designed to not have homology to genomic targets in human, mouse, and rat.
IDT scientists have also computationally designed and tested negative control guide RNA for the Alt-R CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) System in human, mouse, and rat cells.
Resources
Frequently Asked Questions
CRISPR genome editing efficiency seems low - any steps to improve this?
In addition, not every sequence associated with a PAM site performs the same. For example, polymorphisms in the protospacer binding site may reduce editing efficiency. Base mismatches also become more detrimental to editing the closer they are to the PAM site.
We recommend that you try 2 or 3 different PAM sites in your gene of interest to identify a site that provides optimal editing efficiency. Also, be sure to include control experiments. Alt-R™ CRISPR-Cas9 HPRT Positive Controls and Alt-R™ CRISPR-Cas9 Negative Controls are available for human, mouse, and rat.
Please feel free to contact us if you need additional assistance; having the results of your control experiments available will facilitate our ability to help you. For more information, go to www.idtdna.com/ContactUs.
I’m seeing cell death after CRISPR RNA transfection. What can I do to prevent this?
You may also try a different transfection reagent, as minor differences in chemistry can impact toxicity. Make sure to look for transfection reagents optimized for RNA to transfect the Alt-R™ CRISPR guide RNAs. We have delivered these reagents successfully into HEK293 cells using RNAiMAX and CRISPRMAX (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for the Alt-R CRISPR guide RNAs. You should empirically optimize transfection reagents for use in other cell lines. Additionally, you may consider electroporation as an alternate delivery method.
It is also possible that your target gene is vital to your cells, and thus its knockout results in cell death. If the Alt-R CRISPR HPRT Positive Control crRNA works and cell death is not observed, it is likely you are working with a vital gene. In this case you may have to try different cell lines or explore gene knock down technologies including DsiRNA or ASOs. Learn more about our Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 System products.
References
- Mean RJ, Pierides A, Deltas CC, Koptides M. Modification of the enzyme mismatch cleavage method using T7 endonuclease I and silver staining. Biotechniques. 2004;36(5):758-760.
- Vouillot L, Thélie A, Pollet N. Comparison of T7E1 and surveyor mismatch cleavage assays to detect mutations triggered by engineered nucleases. G3 (Bethesda). 2015;5(3):407-415.