Dicer-Substrate Short Interfering RNAs (DsiRNAs) and TriFECTa® Kits
DsiRNAs are 27mer duplex RNAs that demonstrate increased potency in RNA interference compared to traditional, 21mer siRNAs. Proprietary design rules produce optimized DsiRNAs that are available only from IDT.
Ordering
- Achieve sustained knockdown of cytoplasmic RNA using low amounts of DsiRNA
- Select from over 320,000 predesigned DsiRNAs or easily generate your own
- Conveniently obtain all of the duplexes you need by ordering DsiRNAs in a TriFECTa RNAi Kit
DsiRNAs and TriFECTa Kits in tubes
Duplexed 27 nt RNA strands. Order as a TriFECTa Kit and receive all the necessary reagents for RNAi.
DsiRNAs in plates
Use the DsiRNA design tool to browse our inventory of predesigned DsiRNAs, generate custom DsiRNAs, or build your own TriFECTa RNAi Kit. If you prefer to create RNA duplexes without the help of these tools, select manual entry.
For non-human in vivo research applications or other applications that require larger amounts of material, contact us.
Product details
What is RNA interference?
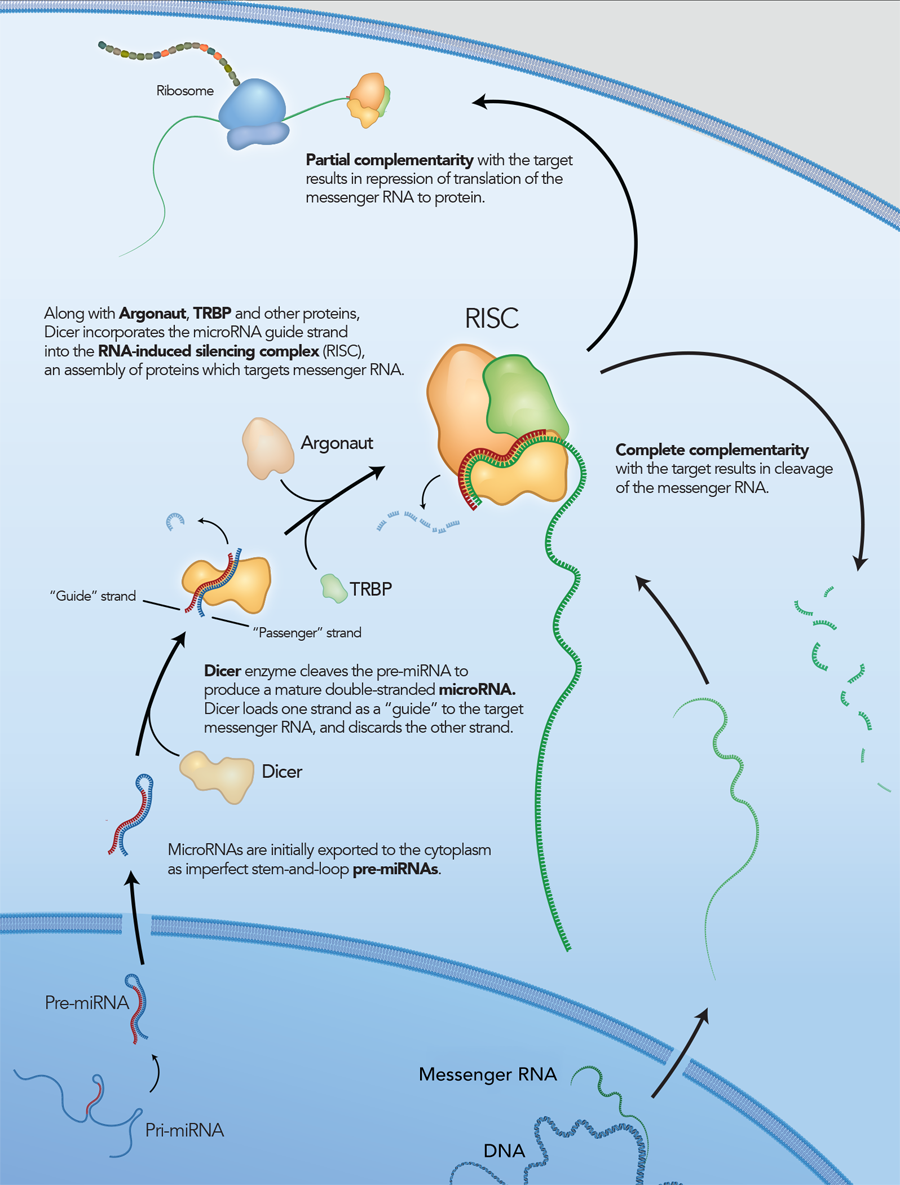
RNA interference is a conserved pathway common to plants and mammals, where double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) suppress expression of genes with complementary sequences [1–2]. Long dsRNAs are degraded by the endoribonuclease Dicer into small effector molecules called siRNAs (small interfering RNAs). siRNAs are approximately 21 bases long with a central 19 bp duplex and 2 base 3′ overhangs. In mammals, Dicer processing occurs as a complex with the RNA-binding protein TRBP. The nascent siRNA associates with Dicer, TRBP, and Argonaut (Ago2) to form the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which mediates gene silencing (Figure 1) [3]. Once in RISC, one strand of the siRNA (the passenger strand) is degraded or discarded, while the other strand (the guide strand) remains to direct sequence selection of the silencing complex. The Ago2 component of RISC is a ribonuclease that cleaves a target RNA under direction of the guide strand.
Although long dsRNAs (several hundred bp) are commonly employed to trigger RNAi in C. elegans or D. melanogaster, these molecules also activate the innate immune system and trigger interferon (IFN) responses in higher organisms. RNAi can be performed in mammalian cells using short RNAs, which generally do not induce IFN responses. Historically, siRNAs have been synthesized as 21mers that bypass the need for Dicer processing by directly mimicking the products that Dicer produces in vivo.
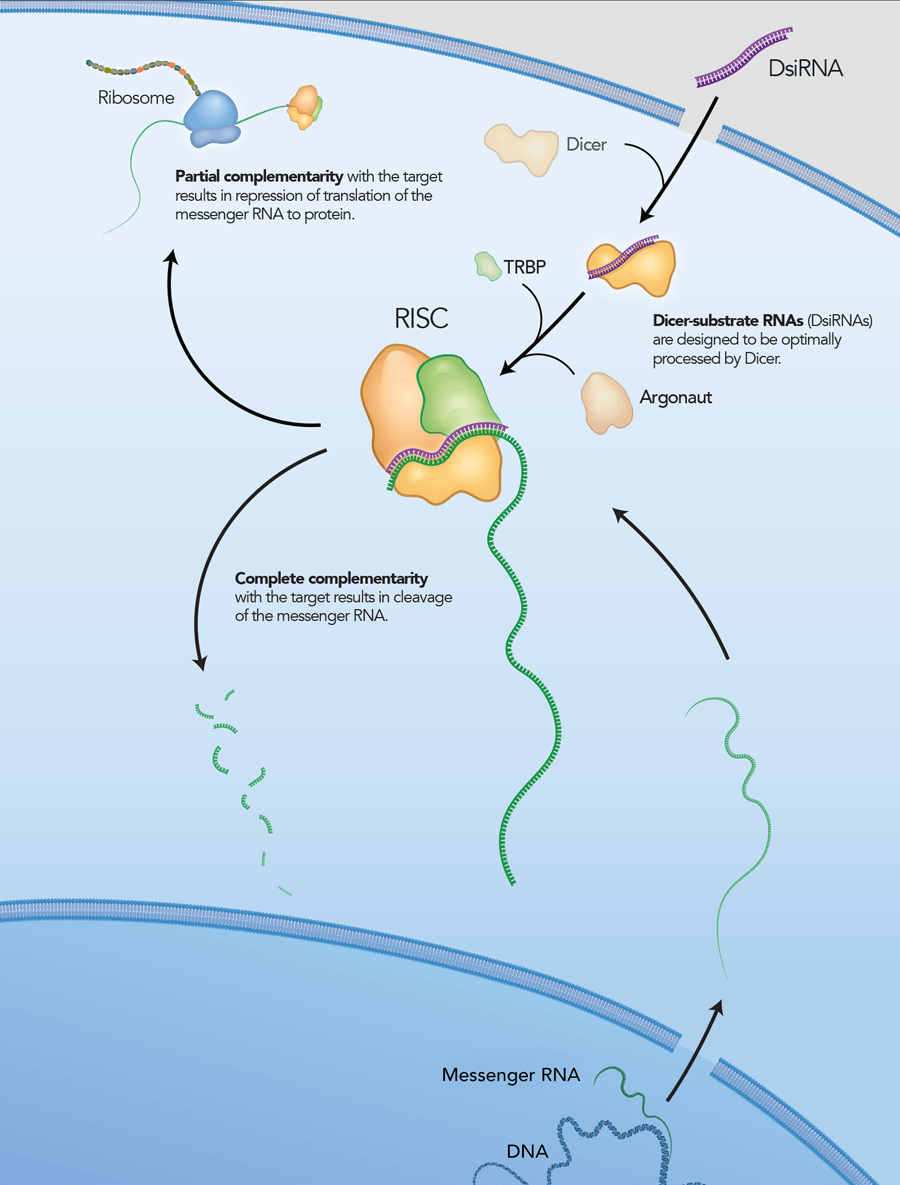
However, it is now thought that, in addition to being a nuclease, Dicer is also required to introduce the siRNA into RISC and is involved in RISC assembly (Figure 2) [4–6]. IDT DsiRNAs are chemically synthesized 27mer RNA duplexes that are optimized for Dicer processing and show increased potency when compared with 21mer siRNAs [7–8]. Dicer-substrate RNAi methods take advantage of the link between Dicer and RISC loading that occurs when RNAs are processed by Dicer.
DsiRNAs
DsiRNAs are chemically synthesized, 27 nt RNA duplexes that are optimized for Dicer processing and are ideal for small-scale in vitro applications. These 27mer duplexes have increased potency in RNAi compared to traditional 21mer siRNAs. DsiRNAs were originally developed as a collaborative effort with Dr John Rossi of the Beckman Research Institute of the City of Hope (Duarte, CA, USA). Updated design rules that have been developed at IDT have resulted in potent DsiRNAs that are available only from IDT. Each DsiRNA is purified and identified by ESI mass spectrometry*. Unless otherwise noted, DsiRNAs are provided dry in tubes. All QC data is provided free of charge on our website.
For ultimate convenience, you can acquire all the necessary reagents for RNA knockdown by ordering your DsiRNAs and controls in a TriFECTa RNAi Kit.
* With the exception of mixed base oligos, which could potentially represent multiple sequences and therefore cannot be accurately evaluated by ESI mass spectrometry.
Predesigned, custom, and control DsiRNAs
Whenever possible, we recommend using predesigned DsiRNAs, as these include significantly more bioinformatics analysis than is possible for DsiRNA sequences designed in real time using the custom design tool. Sequences for all predesigned DsiRNA ordered are provided after purchase.
Predesigned DsiRNAs
Over 322,000 predesigned DsiRNAs have been designed against the human, mouse, and rat transcriptomes (RefSeq Genbank collection: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/RefSeq). With our online design and ordering tool, you can search for predesigned DsiRNAs by gene symbol or NCBI RefSeq accession number. Once you have selected your DsiRNA, the tool will perform automated site selection using a proprietary algorithm that integrates 21mer siRNA design rules and updated criteria specific for 27mers.
Additional analysis is performed to check that the chosen sites do not target alternatively spliced exons and do not include known single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Sequences are also examined to minimize the potential for cross-hybridization and off-target effects (Smith-Waterman analysis). If plan to use 24 or more DsiRNAs, you reduce costs by ordering a multi-reaction plate of DsiRNAs (2 or 10 nmol of each DsiRNA).
TriFECTa RNAi Kit
With the TriFECTa Kit, you receive all of the duplexes you need for successful RNA knockdown. These include:
- 3 Predesigned DsiRNAs that are specific for a single target gene
- 3 control DsiRNAs for optimizing your RNAi experimental setup:
- TYE 563 Transfection Control DsiRNA, 1 nmol
- HPRT-S1 Positive Control DsiRNA, 1 nmol
- Negative Control DsiRNA, 1 nmol
- Nuclease-Free Duplex Buffer (2 mL) for resuspending your DsiRNAs, which are delivered dry
TriFECTa Kit guarantee
We guarantee that at least 2 of the 3 DsiRNAs in your TriFECTa Kit will give you ≥70% knockdown of your target mRNA when:
- The DsiRNA is used at 10 nM concentration and assayed by qPCR
- Fluorescent transfection control experiments indicate >90% of cells have been transfected
- The HPRT positive control DsiRNA works with the expected efficiency
Custom DsiRNAs
You can use our online DsiRNA tool to select DsiRNAs which target sequences in species other than human, mouse, or rat. To do so, first click “Generate Custom DsiRNA” within the tool, and then enter a NCBI RefSeq accession number or FASTA sequence.
Control DsiRNAs
Our DsiRNAs are compatible with all common transfection methods, including cationic lipids, liposomes, and electroporation. However, certain methods may be more efficient than others depending on your cell line. Before undertaking studies of new targets, it is best practice to optimize your RNAi experimental system with these controls.
- Transfection efficiency controls (Cy®3, TEX 615, and TYE 563-labeled DsiRNAs): Dye-labeled, transfection efficiency control DsiRNAs allow for rapid, easy examination of many reagents or conditions in parallel. We recommend optimizing transfection conditions for each cell line studied and for each form of nucleic acid used (large DNA plasmids, for example, often require different transfection conditions than short DsiRNAs). It may also be necessary to empirically test different transfection reagents (or other approaches) to establish a protocol that performs optimally with each cell line used.
- Endogenous gene positive controls and qPCR assays (HPRT-S1 DsiRNAs and qPCR assays): It is possible to get good DsiRNA uptake without delivering your oligos to the correct cytoplasmic location for effective RNAi. We recommend testing for functional knockdown using a positive control DsiRNA after checking for efficient transfection. With good transfection, 10 nmol HPRT-S1 positive control DsiRNA will reduce HPRT mRNA levels by >90% after 24 hours. Since knockdown of HPRT can slow cell growth and affect cell viability for incubation periods >72 hours, it is important to examine your cells at 24 or 48 hr timepoints. Due to sequence similarity, the HPRT-S1 control DsiRNA can be used in human, mouse, rat, and Chinese hamster (CHO) cells. Other genomes may require custom controls. To confirm functional activity, use HPRT qPCR assays to measure HPRT mRNA expression levels in human and mouse cells.
- Exogenous reporter gene controls (DsiRNAs against EGFP or Luciferase): Depending on your cell line, knockdown of reporter genes can be used as either positive or negative controls. For cell lines that express EGFP or Luciferase reporter gene (either stably or by co-transfection of an expression plasmid), DsiRNAs targeting the respective reporter gene will serve as positive controls. However, for cell lines that do not express EGFP or Luciferase reporter genes, DsiRNAs targeting the respective gene will serve as negative controls. Due to their efficient RISC loading, using confirmed DsiRNAs as functional reporter gene controls offer more control than non-targeting sequences.
- Universal negative controls (non-targeting and scrambled DsiRNAs): The Negative Control DsiRNA is a non-targeting DsiRNA that will not interact with any sequences in the human, mouse, or rat transcriptomes. If making a choice, we recommend using the Negative Control DsiRNA, instead of the Scrambled Negative Control DsiRNA. For cells that do not express the respective reporter gene, the EGFP and luciferase DsiRNAs may be used as negative controls if functional, targeting DsiRNA are desired (see Exogenous reporter gene positive controls, above).
Product data
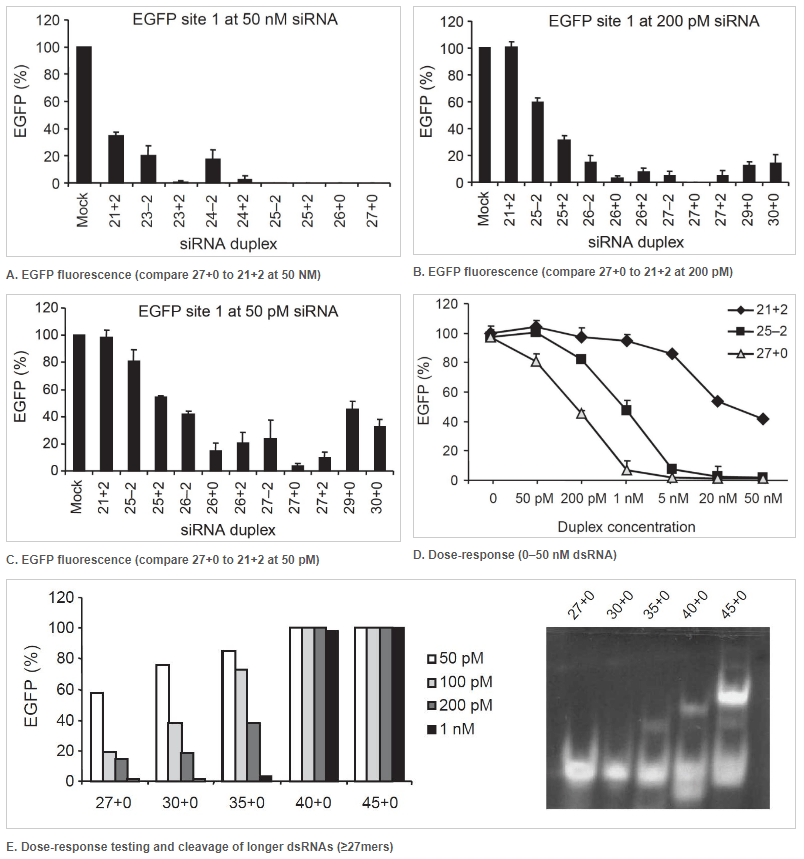
27 nt DsiRNAs are more potent effectors of RNAi than 21 nt siRNAs
Figure 1. 27mer DsiRNAs (27+0) are more potent effectors of RNAi than a 21mer siRNA (21+2). Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) names: number of duplexed bases + number of 3′ overhanging bases or – number of 5′ overhanging bases. Each graph point represents the average of 3 independent measurements. (A–D) EGFP expression levels were determined after cotransfection of HEK293 cells with a fixed amount of EGFP expression plasmid and various concentrations of dsRNAs of varying length. Transfections were performed using (A) 50 nM, (B) 200 pM, and (C) 50 pM of the indicated dsRNAs. Error bars indicate the standard deviation. (D) Dose-response testing of dsRNAs. (E) Left: Dose-response curve of longer dsRNAs transfected into NIH3T3 cells that stably express EGFP. Right: Using an in vitro Dicer cleavage assay to analyze Dicer processing of longer dsRNAs. DsiRNAs and cleavage products are shown in this 15% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel
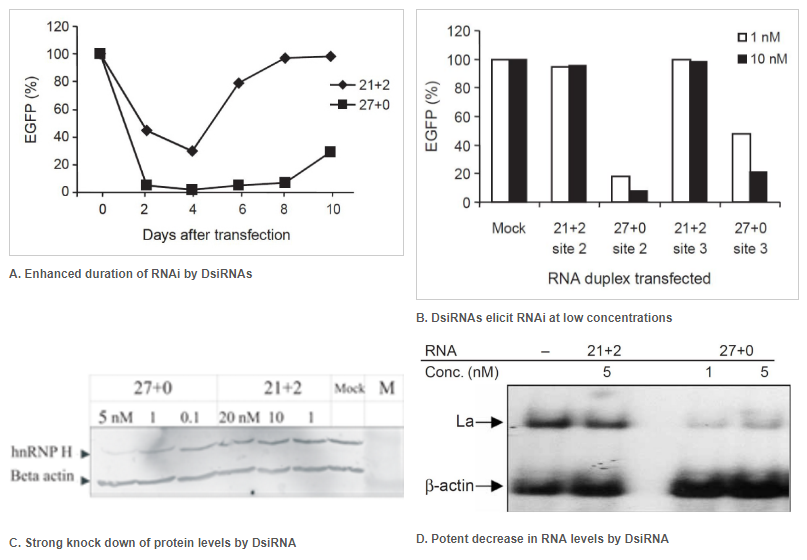
Figure 2. Enhanced duration of RNAi at lower concentrations when comparing 27mer DsiRNA (27+0) to 21mer siRNA (21+2). Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) names: number of duplexed bases + number of 3′ overhanging bases. (A) Enhanced duration of RNAi by DsiRNAs (up to 10 days) compared to siRNA (approximately 4 days): 5 nM of DsiRNA or siRNA were transfected into NIH3T3 cells stably expressing EGFP. Duplicate samples were taken on the indicated days, and EGFP expression was determined by fluorometry. (B) DsiRNAs can elicit RNAi at low concentrations compared to siRNAs. EGFP expression was determined after dsRNAs were transfected along with the EGFP reporter construct. Target names: site-2 is EGFP-S2 and site-3 is EGFP-S3, which were both targets known to be refractory to RNAi using siRNA. (C, D) Comparison of DsiRNA and siRNA in downregulation of endogenous transcripts (that is, hnRNP H mRNA or La mRNA). (C) hnRNP H knockdown was assayed by western blot and (D) La knockdown by northern blot analyses. The dsRNAs were used at the indicated concentrations. β-Actin was used as an internal control and loading standard.
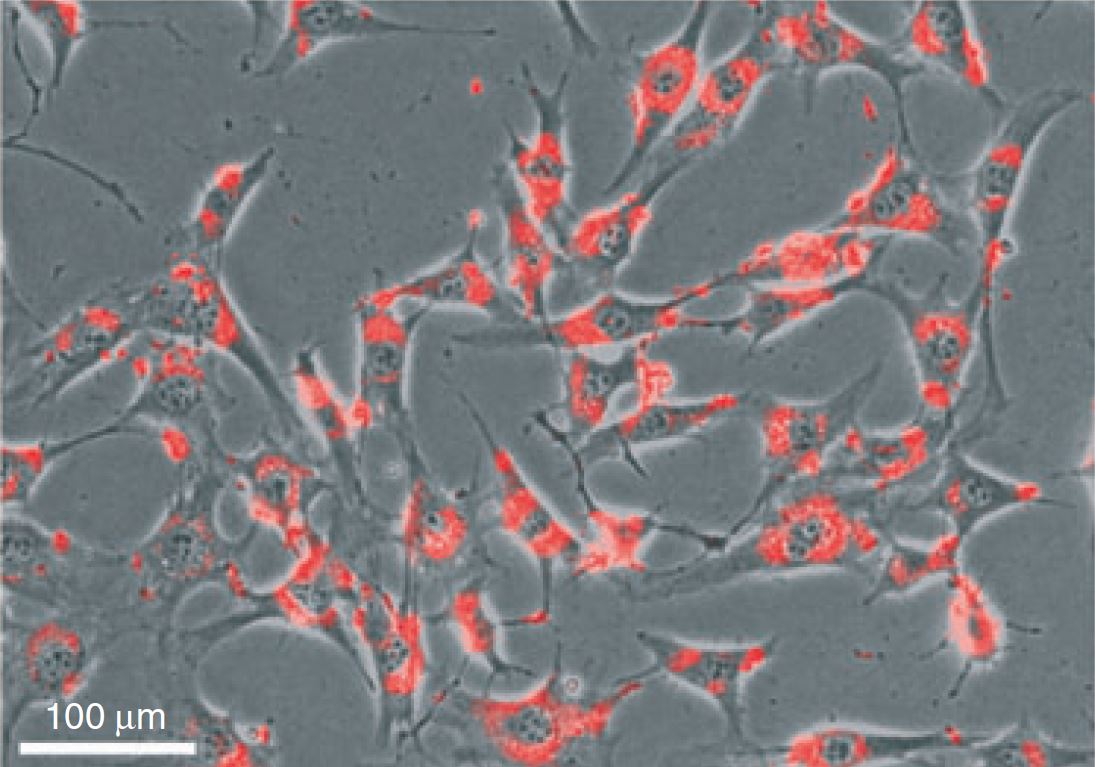
Track DsiRNA transfection efficiency with Transfection Control DsiRNAs
Assess RNAi function with Positive and Negative Control DsiRNAs
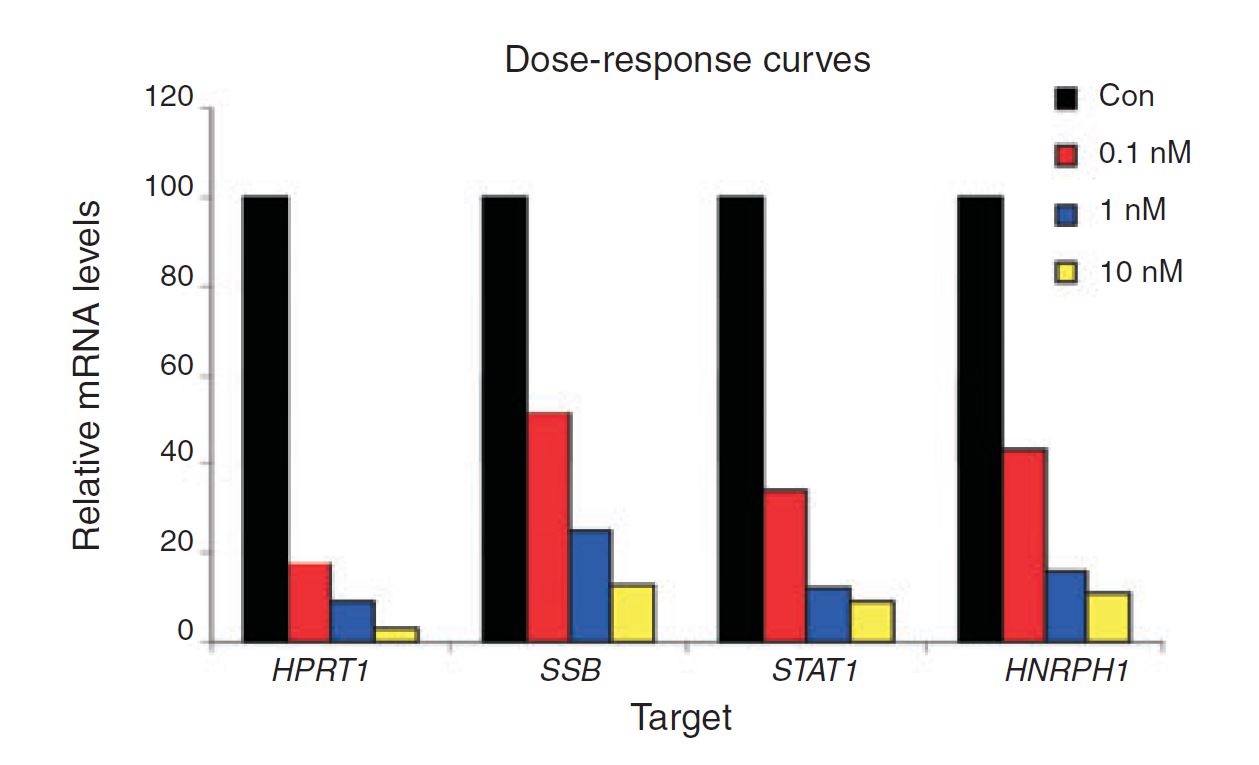
Figure 4. Negative control DsiRNA during dose optimization determine baseline. HeLa cells were transfected using TriFECTa DsiRNAs specific for HPRT1, SSB, STAT1, and HNRPH1 at the concentrations indicated. Relative mRNA levels were measured using qRT-PCR at 24 hr after transfection; data were normalized against an internal RPLP0 control using the Scrambled Negative Control DsiRNA (Con) as baseline (100%).
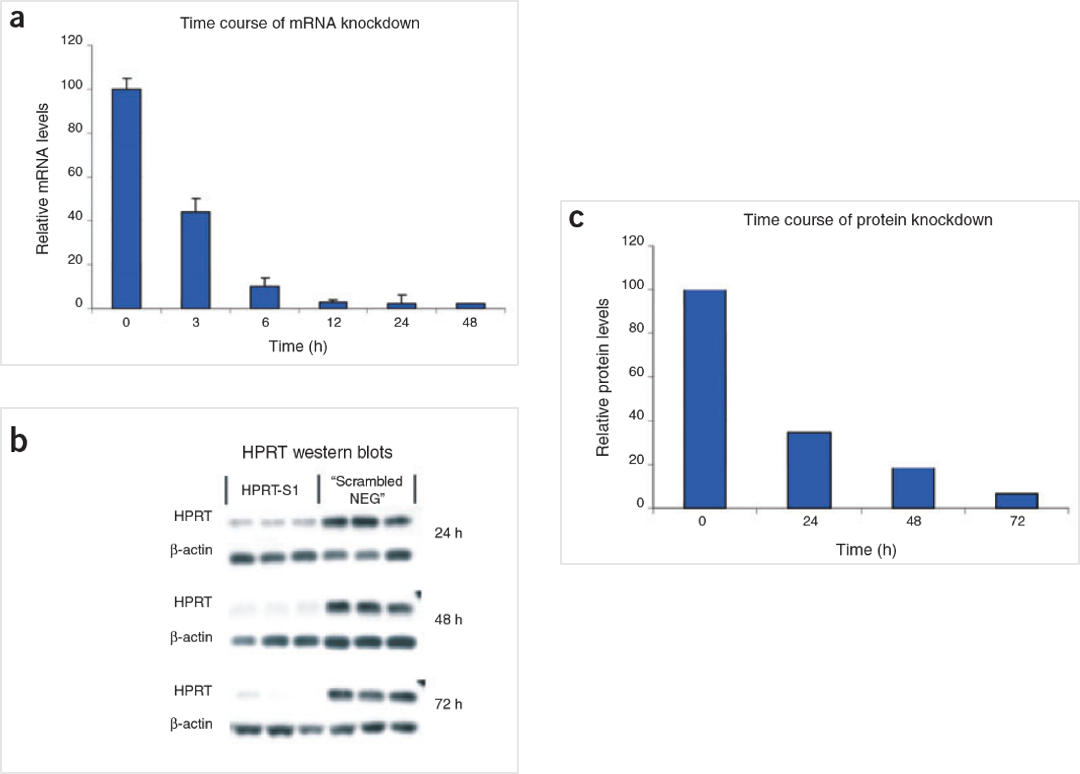
Figure 5. The HPRT Positive Control DsiRNA delivers strong knockdown of mRNA and protein. HeLa cells were transfected with HPRT S1 Positive Control DsiRNA (10 nM) and analyzed at the indicated time points. (A) HPRT mRNA amounts were measured by qRT-PCR. (B) HPRT protein levels were assessed by western blot; β-actin loading standard is shown. Each lane represents a separate transfection. (C) HPRT protein levels were averaged, and relative knockdown at the indicated times after transfection was quantified
GMP and OEM
If you require oligos that are approved for use in molecular diagnostic applications, or if you are interested in our OEM services, please click here.
GMP refers to products manufactured under ISO 13485: 2016 QMS. Purchaser is solely responsible for all decisions regarding the use of these products and any associated regulatory or legal obligations for their legal marketing.
Resources
Frequently asked questions
Which negative control Dicer-substrate siRNA (DsiRNA) should I choose, DS NC1 or DS ScrambledNeg?
We strongly recommend using the DS NC1 negative control duplex. This has been extensively bioinformatically assessed, and has no activity in human, mouse, and rat cells. The DS ScrambledNeg sequence is an older control that has been kept as a legacy product for customers who have had success with it in their cell lines.
Learn more and order from the Dicer-Substrate siRNA (DsiRNA) page.
Which is the best way to deliver oligos into cells in culture?
The best method depends on the type of cells and types of modifications on the oligo, as well as the intended use of the ASO. Contact us for more information.
What is the difference between 27mer siRNAs (DsiRNAs) and traditional 21mer siRNAs?
The 27mer Dicer-substrate siRNAs (DsiRNAs) are designed for optimal processing by Dicer and show increased potency by engaging this natural processing pathway.
What is the Design or Catalog ID # for my DsiRNA?
DsiRNAs designed and ordered since February 2016
Example Design ID # hs.Ri.BRCA1.13.2:
- “hs” indicates the species, Homo sapiens (human). Similarly, “mm” means Mus musculus (mouse), “rn” means Rattus norvegicus (rat), and “CD” indicates custom design.
- “Ri” indicates this is an RNA interference (DsiRNA) product.
- “BRCA1” indicates the NCBI gene symbol, in this example, the breast cancer associated 1 gene.
- “13” indicates that this sequence comes from the 13th iteration of the DsiRNA designs. Custom designs have a unique identifying number.
- “2” indicates that this was the second design in the search results.
DsiRNAs designed and ordered before February 2016
Example Catalog ID # HSC.RNAI.N000546.12.6_2nm:
- “HSC” indicates that it is “Homo sapiens common”, meaning that if there is more than one splice form in RefSeq, this sequence is common to all forms. Similarly, “HSS” means “Homo sapiens specific” to a single splice variant.
- “RNAI” indicates that this is a DsiRNA product.
- “N000546” indicates the RefSeq gene accession number, which is NM_000546 (gene symbol TP53) in this example.
- “12” indicates that this sequence comes from the 12th iteration of the DsiRNA designs.
- “6” denotes that this was the 6th in the list of 10 predesigned DsiRNAs and identifies which DsiRNA in the predesigned library was ordered.
- “2nm” indicates that a 2 nmol scale was ordered.
What guarantees are associated with the TriFECTa kit? Is the Predesigned DsiRNA specific?
Our Bioinformatics Department does a full screening of sequence designs before adding them to the database. This includes performing a BLAST search of the sequences to ensure they will only target the gene in question, performing secondary structure checks, and making sure the end stabilities are favorable for incorporation into the RISC complex.
What DsiRNA concentration do I need to use in my experiment to see knockdown?
For an RNAi or antisense experiment, the actual level of target gene knockdown is related to the transfection efficiency. A positive control such as HPRT DsiRNA should be used in each experiment to assess transfection efficiency.
In addition, IDT recommends using a dose-response curve of 0.1, 1, and 10 nM to determine maximum response.
How do I order siRNA oligos?
We offer traditional 21mer duplex RNAs as well as 27mer, Dicer-substrate RNAs (DsiRNAs), which engage the Dicer enzyme natural siRNA processing pathway.
If you know the sequence you want to order, you can order traditional siRNAs from the Order tab at https://www.idtdna.com/ by selecting Main Menu>Custom RNA Oligos.
DsiRNAs can be ordered at https://www.idtdna.com/site/order/duplexentry/index/dicer. See the DsiRNA selection tool that can be accessed under "Gene Silencing" on the Products tab of our website.
Do you provide any nonsilencing (negative) controls for Dicer-substrate siRNAs (DsiRNAs)?
We currently offer 2 nonsilencing, negative control DsiRNAs that do not recognize any sequences in human, mouse, or rat transcriptomes, a nontargeting DsiRNA (DS NC1) and a DsiRNA with a scrambled sequence (DS ScrambledNeg).
We strongly recommend using the DS NC1 negative control duplex. This has been extensively bioinformatically screened, and has no activity in human, mouse, and rat cells. The DS ScrambledNeg sequence is an older control that has been kept as a legacy product for customers who have had success with it in their cell lines.
Do the positive and negative controls in the TriFECTa kit come with primers and RT-PCR materials?
The kit does not include primers or PCR reagents for quantification of gene silencing. Separately, we offer primer sets for targeting human or mouse HPRT for use in SYBR® Green–based qPCR assays to monitor RNAi function following transfection with the HPRT-S1 Positive Control DsiRNA.
For other human, mouse, or rat targets, consider using Predesigned PrimeTime™ qPCR Sequences . For additional species, you can easily design a custom PrimeTime qPCR Assay using our free, online PrimerQuest™ Tool.
The TriFECTa Kit includes:
- 3 target-specific Dicer-Substrate siRNAs (DsiRNAs, 2 nmol each)
- 1 negative control DsiRNA (NC1, which does not target any human, mouse, or rat sequence)
- 1 positive control DsiRNA (HPRT-S1 DS Positive Control)
- 1 fluorescent transfection control DsiRNA (TYE 563-labeled transfection control)
- Nuclease-Free Duplex Buffer
IDT recommends that the qPCR assay be located close to site of the DsiRNA target sites to avoid measuring a cleaved transcript that has a remaining fragment.
Are your Dicer-substrate siRNAs (DsiRNAs) provided ready to use, and do I need to order a transfection reagent separately?
Our scientists have had success with Lipofectamine® RNAiMax (Thermo Fisher Scientific), Oligofectamine™ (Thermo Fisher Scientific), siLentFect™ (Bio-Rad), TransIT-TKO® (Mirus Bio), and other cationic-lipid transfection products. The choice of transfection reagent depends on the cells being used and should be optimized in your lab.
References
- Hannon GJ, Rossi JJ. (2004) Unlocking the potential of the human genome with RNA interference. Nature, 431:371–378.
- Meister G, Tuschl T (2004) Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature, 431:343–349.
- Chendrimada TP, Gregory RI, et al. (2005) TRBP recruits the Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing. Nature, 436:740–744.
- Lee YS, Nakahara K, et al. (2004) Distinct roles for Drosophila Dicer-1 and Dicer-2 in the siRNA/miRNA silencing pathways. Cell, 117:69–81.
- Pham JW, Pelllino JL, et al. (2004) A Dicer-2-dependent 80s complex cleaves targeted mRNAs during RNAi in Drosophila. Cell, 117:83–94.
- Tomari YC, Matranga C, et al. (2004) A protein sensor for siRNA asymmetry. Science, 306:1377–1380.
- Kim DH, Behlke MA, et al. (2005) Synthetic dsRNA Dicer-substrates enhance RNAi potency and efficacy. Nat Biotechnol, 23(2):222–226.
- Rose SD, Kim DH, et al. (2005) Functional polarity is introduced by Dicer processing of short substrate RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res, 33(13):4140–4156.
- Rose SD, Collingwood MA, Behlke MA (2006) Optimizing knockdown of gene expression using the TriFECTa™ Dicer-substrate RNAi reagent system. Nat Methods 3, V–VII.