CRISPR nucleases
Recombinant, high-purity endonucleases for genome editing experiments
Choose from Cas9 (Streptococcus pyogenes) and Cas12a (Cpf1; Acidaminococcus sp. BV3L6, or Lachnospiraceae bacterium ND2006) proteins.
Ordering
- Nuclear localization signals (NLSs) increase genome editing efficiency
- Use as part of a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex
- High-purity enzymes
Custom CRISPR solutions
Don’t see what you’re looking for? We are continually expanding our CRISPR product line, and we may have what you need. If you are interested in custom libraries, other CRISPR enzymes, formulations, or other CRISPR tools, contact our CRISPR experts today to discuss customized solutions for your research: CRISPR@idtdna.com.
Product Details
Which Cas9 enzyme to use
Comparison of Alt-R Cas9 Nucleases and Nickases. Click here to download PDF version.
Alt-R S.p. Cas9 nuclease
Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 is the standard Cas9 used for general genome editing. It is a high purity, recombinant S. pyogenes Cas9. The enzymes include nuclear localization sequences (NLSs) and C-terminal 6-His tags. The S. pyogenes Cas9 enzyme must be combined with a gRNA to produce a functional, target-specific editing complex. For the best editing, combine the Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 enzyme with Alt-R CRISPR gRNA in equimolar amounts.
Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 nuclease
Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3 is also used for general genome editing, but it offers improved specificity over wild-type Cas9, greatly reducing the risk of off-target cutting events. This Cas9 variant also preserves the high level of editing efficiency expected from a Cas9 nuclease, maintaining 90–100% on-target editing activity at most sites. For applications that are sensitive to off-target events, combining the Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3 with the optimized Alt-R CRISPR‑Cas9 gRNA (crRNA:tracrRNA) is highly recommended.
Alt-R S.p. Cas9-GFP (or RFP) nuclease
The Alt-R S.p. Cas9-GFP V3 and S.p. Cas9-RFP V3 nucleases are high purity, recombinant S. pyogenes Cas9 enzymes that are expressed as fusion proteins with nuclear localization sequences (NLSs) and C-terminal 6-His tags. These enzymes have on-target functionality comparable to wild-type S.p. Cas9 and are designed for applications that require post‑transfection visualization of the protein or enrichment of edited cells using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). These enzymes should be combined with Alt-R CRISPR gRNA in equimolar amounts.
Alt-R S.p. Cas9 nickases
Cas9 nickases allow specific cutting of only one strand at the DNA target site. Cuts to both strands of DNA are accomplished by using either Alt-R S.p. Cas9 D10A Nickase V3 or Alt-R S.p. Cas9 H840A Nickase V3, with two gRNAs that target two neighboring Cas9 sites, one on either strand of the target region. There are two main reasons to consider using nickases. First, the use of two neighboring gRNAs instead of one gRNA (as used with Alt-R S.p. Cas9) can decrease off-target effects. Second, the rate of HDR is increased. For more information about using Cas9 nickases, see the application note.
Alt-R S.p. dCas9 protein
Alt-R S.p. dCas9 Protein V3 has mutations that result in the loss of nuclease activity. This protein can form RNP complexes with Alt-R gRNAs and bind to the target region specified by the gRNA without cutting the DNA. The primary use of dCas9 protein is to block transcription at a specific site on the genome. This is known as CRISPRi and is an alternative to RNAi for knockdown instead of knockout of genes.
Like the other Alt-R enzymes, Alt-R S.p. dCas9 Protein V3 is provided as 10 mg/mL in 50% glycerol, and it can be diluted in PBS or Opti-MEM media before use.
Cas12a (Cpf1) proteins
Alt-R A.s. Cas12a (Cpf1) V3 nuclease
Alt-R A.s. Cas12a (Cpf1) Nuclease V3 enzyme is a high purity, recombinant Acidaminococcus sp. BV3L6 Cas12a. It is useful for targeting AT-rich regions when the Cas9-specific PAM sequence (NGG) is not available. The enzymes include nuclear localization sequences (NLSs) and C-terminal 6-His tags. The Cas12a enzyme must be combined with a gRNA to produce a functional, target-specific editing complex. For the best editing, combine Alt-R A.s. Cas12a (Cpf1) Nuclease V3 enzyme with optimized Alt-R CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) crRNA in equimolar amounts.
Attention: Unlike S. pyogenes Cas9, which cleaves most NGG PAM sites to some degree, some of the tested TTTV sites show no cleavage by A.s. Cas12a nuclease. We recommend using positive control crRNAs to establish that your cells can be edited by Cas12a. In addition, we suggest testing 3 or more crRNAs per target gene.
Alt-R A.s. or L.b. Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra Nucleases
The Alt-R Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra Nucleases are also useful for targeting AT-rich regions without available Cas9-specific PAM sequences. However, they have much higher on-target potency than wild-type A.s. Cas12a (Cpf1). The Alt-R Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra also can recognize many TTTT PAM sites in addition to TTTV motifs, increasing target range for genome editing studies. Furthermore, the new Alt-R Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra nucleases are active at room temperature, making them flexible tools for applications requiring delivery at lower temperatures.
Comparison of CRISPR genome editing using Cas9 vs. Cas12a (Cpf1)
| Cas9 system | Cas12a system | |
|---|---|---|
| Applications |
|
|
| Ribonucleoprotein components |
|
|
| Variants |
|
|
| Cas9 crRNA:tracrRNA (option 1) | crRNA
tracrRNA
| — |
| Cas9 sgRNA (option 2) |
| — |
| Cas12a crRNA | — |
|
| CRISPR enzyme |
|
|
| DNA cleavage |
|
|
| PAM sequence† |
|
|
| Current recommendations for Alt-R RNP delivery |
|
|
* Molecular weight of Alt-R nuclease
† N = any base; V = A, C, or G
This comparison table is available for download (see page 2).
Product Data
Cas9 Nuclease
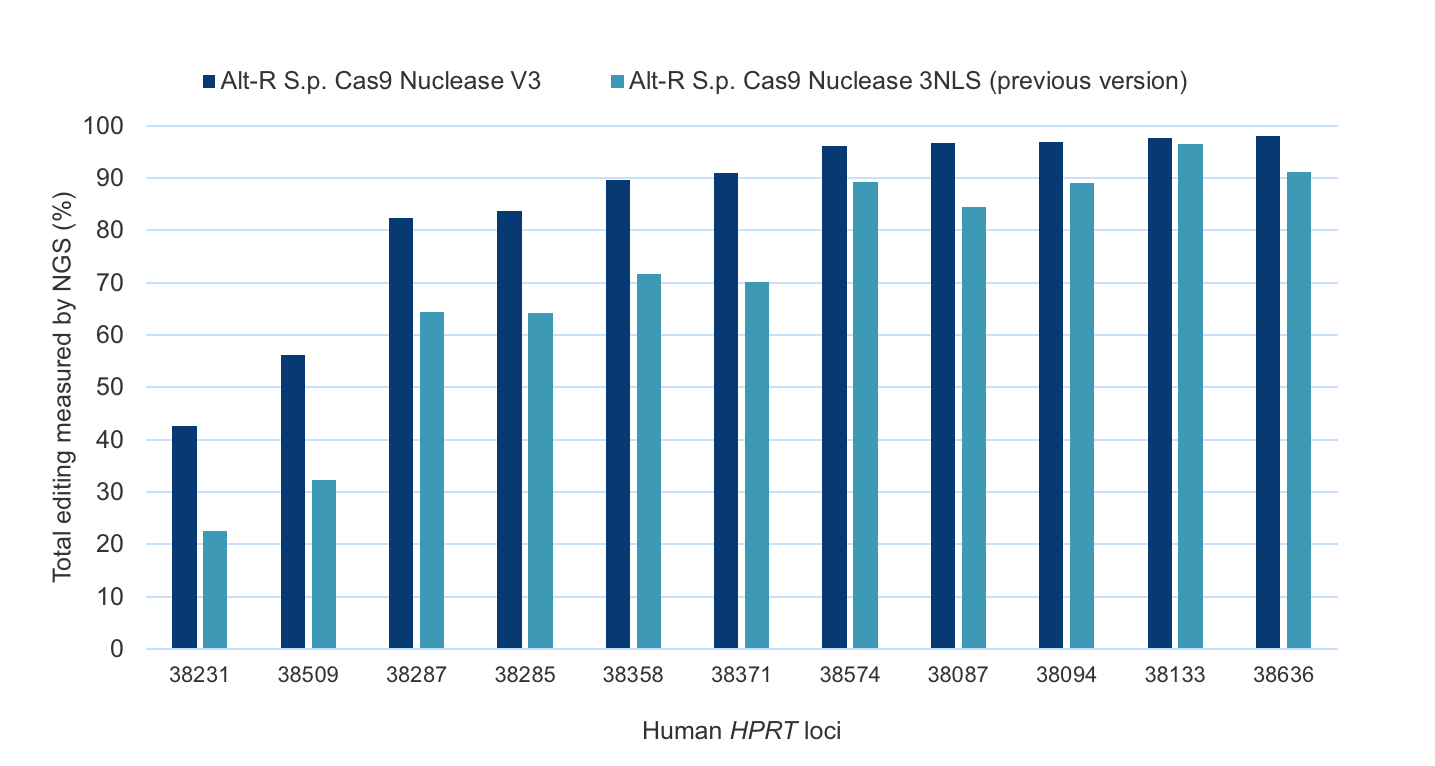
Improved editing efficiency using Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3
Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 is designed to maximize the efficiency of genome editing across a broad number of sites. Modification of the expression construct facilitates nucleus-targeted delivery, resulting in enhanced cleavage, particularly at difficult targets (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 genome editing efficiency even at challenging target sites. Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes were formed with 1 of the 2 wild-type Cas9 proteins—Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease 3NLS (light blue) or Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 (dark blue), combined with an Alt-R crRNA:tracrRNA complex targeting one of 11 loci on the human HPRT gene. RNP complexes (4 µM) were delivered into HEK-293 cells by nucleofection. Total editing at the on-target loci was calculated by NGS. n = 1.
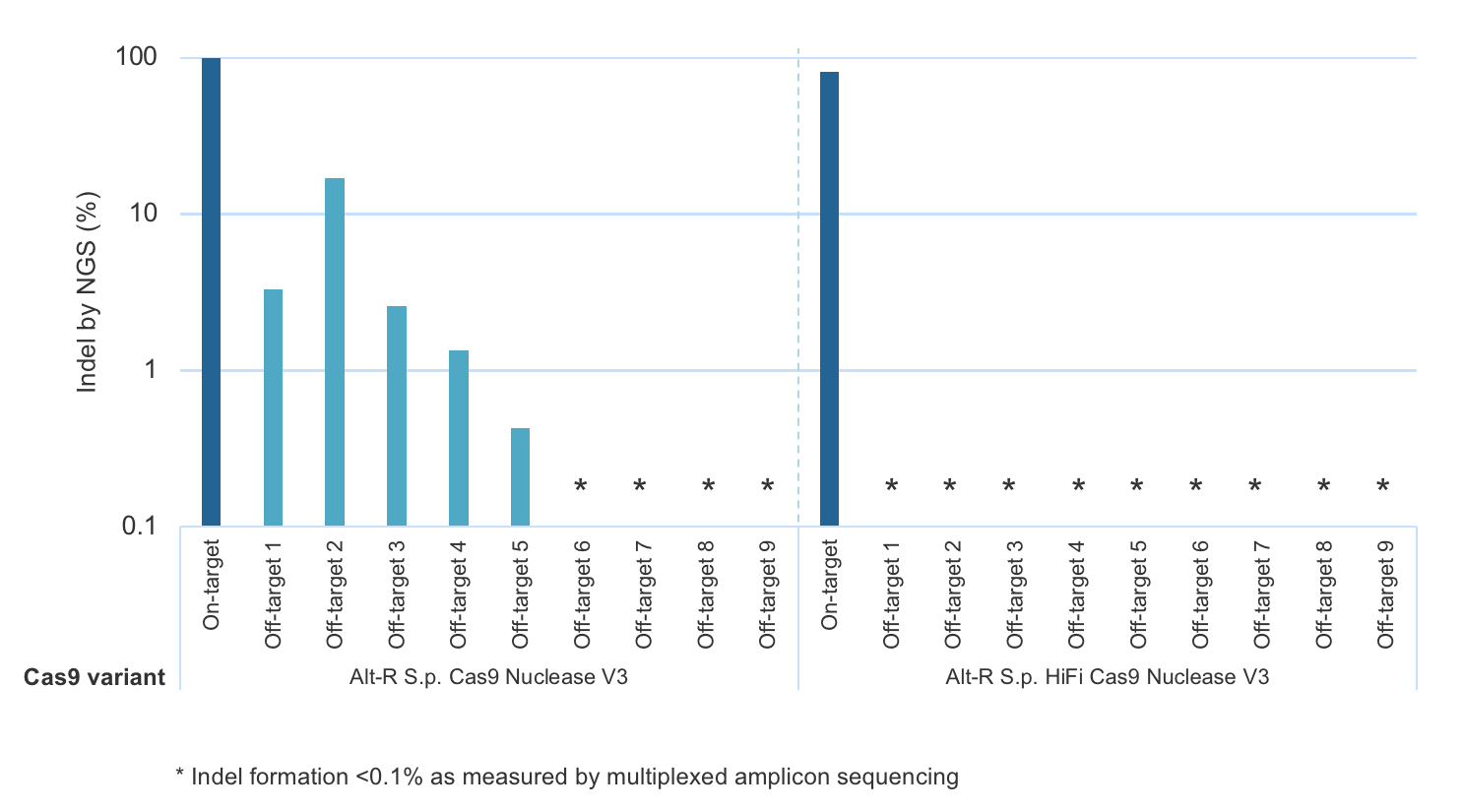
Increased specificity using Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3
As with the wild-type Alt-R Cas9 Nuclease V3, modification of the expression construct facilitates nucleus-targeted delivery, resulting in enhanced on-target cleavage by Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3. However, Alt-R HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3 also provides superior cutting specificity (minimized off-target editing; Figure 2).
Figure 2. Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3 facilitates near-WT on‑target editing potency and reduces off-target site editing. RNP complexes were formed with either Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 or Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3, combined with an Alt-R crRNA:tracrRNA complex targeting the EMX1 gene. RNP complexes (4 µM) were delivered into HEK-293 cells via nucleofection. Indel formation at the on-target locus as well as nine known off-target sites were measured by NGS (indicated on the y axis in log scale). n = 1.
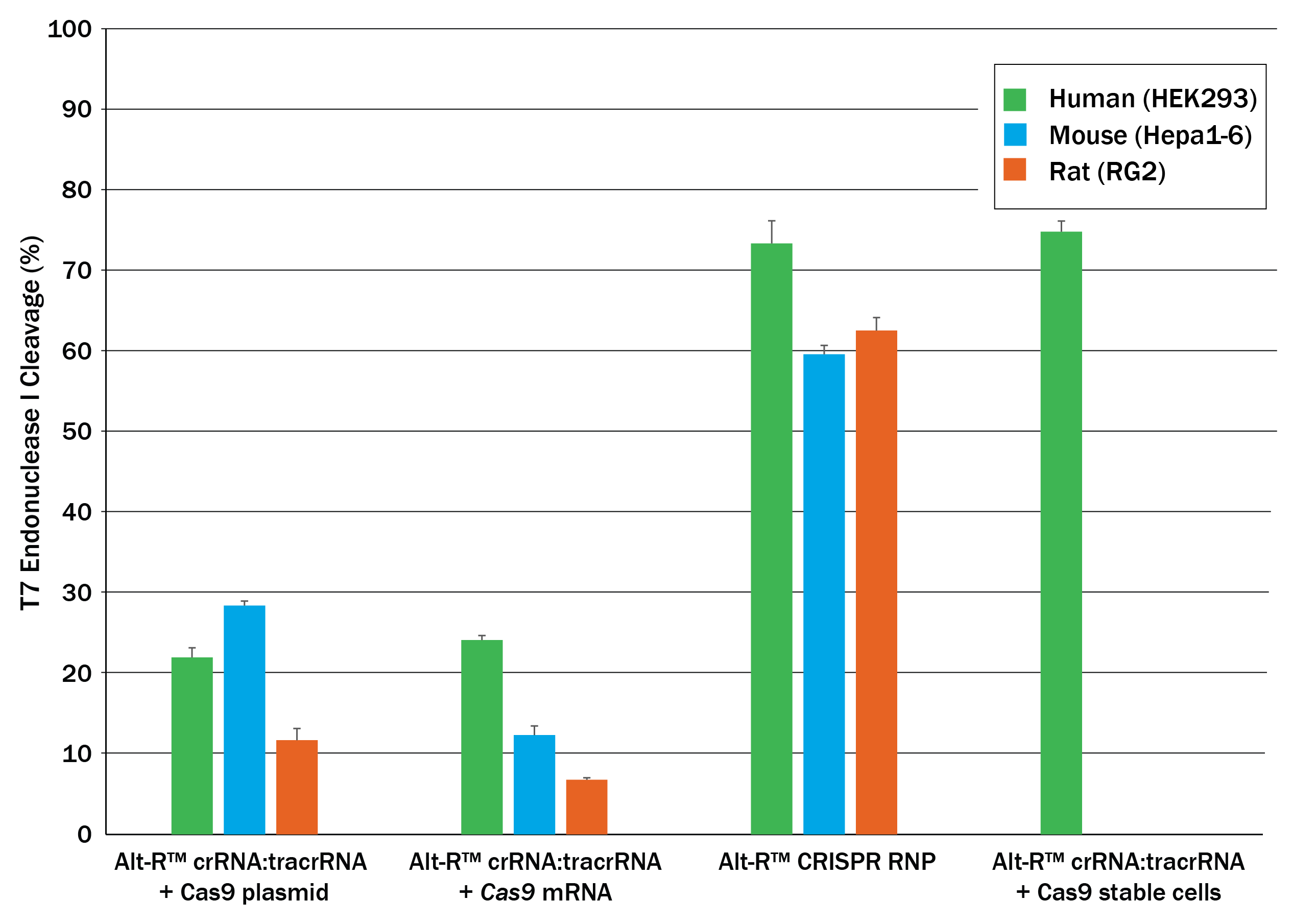
Potent editing with the Alt-R S.p. Cas9 nucleases
The Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 System includes potent Alt-R S.p. Cas9 nucleases. When Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease 3NLS was combined with the Alt-R CRISPR crRNA and tracrRNA into a ribonucleoprotein (RNP), the system outperformed other editing approaches (Figure 3). You can expect even better editing efficiency with Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 (see Figure 2). RNP transfections also provide control of amount of editing complexes used, and the non-renewable Cas9 RNP is cleared after a short duration by endogenous mechanisms, limiting off-target editing.
Figure 3. Experiment showing that lipofection of Alt-R CRISPR‑Cas9 System components as a ribonucleoprotein outperforms other transient CRISPR-Cas9 approaches. Alt-R CRISPR HPRT Control crRNA complexes for human, mouse, or rat were complexed with Alt-R CRISPR tracrRNA. Resulting complexes were transfected with Cas9 expression plasmid, Cas9 mRNA, or as part of a Cas9 RNP (containing Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease 3NLS, pre-complexed with the crRNA and tracrRNA) into human (HEK-293), mouse (Hepa1-6), or rat (RG2) cell lines. The Cas9 RNP outperformed the other transient Cas9 expression approaches, and performed similar to reference HEK293-Cas9 cells that stably express S. pyogenes Cas9. Error bars represent SD, n = 3.
IDT’s Alt-R S.p. Cas9-GFP and Alt-R S.p. Cas9-RFP nucleases maintain consistent on‑target activity
Figure 4. IDT fluorescent CRISPR proteins maintain consistent on-target activity across multiple guides. Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 sgRNAs were designed to target NGG PAM sites within the human HPRT gene. Guides were complexed with Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3, Cas9-GFP, or Cas9-RFP to form RNPs. RNPs were then delivered into HEK293 cells using the Lonza 96 well shuttle nucleofector at a concentration of 2.0 µM. After 48 hrs, genomic DNA was isolated (QuickExtract™ solution, Epicenter), and editing was assessed by T7El mismatch endonuclease assay. Error bars represent SD, n = 3.
As shown in Figure 5, Alt-R fluorescent CRISPR nucleases enable enrichment of edited cells by fluorescent activated cell sorting (FACS).
Figure 5. Fluorescent CRISPR proteins can be used to enrich for edited cells by fluorescence activated cell sorting. (A) RNPs consisting of either Cas9-GFP or Cas9 V3 complexed with CRISPR‑Cas9 sgRNAs targeting two sites in the HPRT gene were delivered into HEK293 cells using either Lipofectamine™ RNAiMAX (Thermo Fisher) at 10 nM RNP or using a Nucleofector™ system (Lonza) at 2 µM RNP. The graphs show the GFP signal versus cell count, where cell count has been normalized to the mode for cells that had either Cas9-GFP or Cas9 V3 delivered using either lipofection or Nucleofection™. (B) Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 sgRNAs were designed to target NGG PAM sites throughout the human genome. Guides were complexed with either Cas9-GFP or Alt-R Cas9 V3. RNPs were delivered into HEK293 cells using Lipofectamine™ RNAiMAX at 10 nM final concentration. After ~18 hrs, cells were sorted using a FACSAria™ II (Becton Dickinson) cell sorter into three subpopulations, GFP High: top 20%, Medium: 80–60%, and Low: Bottom 60% of cells based on GFP signal. Cells were then replated, and genomic DNA was isolated after 48-72 hrs. Editing was analyzed by NGS, n = 1. (C) Confocal images of HEK293 cells taken approximately 18 hours after delivery of either Cas9-GFP or Alt-R Cas9 V3 protein complexed with Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 sgRNA delivered by Nucleofection™ at 2 µM RNP. Prior to imaging, live cells were incubated with Hoechst 33342 and washed with PBS. Cells were imaged in complete media in a chambered coverglass using a Leica SP8 confocal microscope.
Cas12a Nuclease (Cpf1)
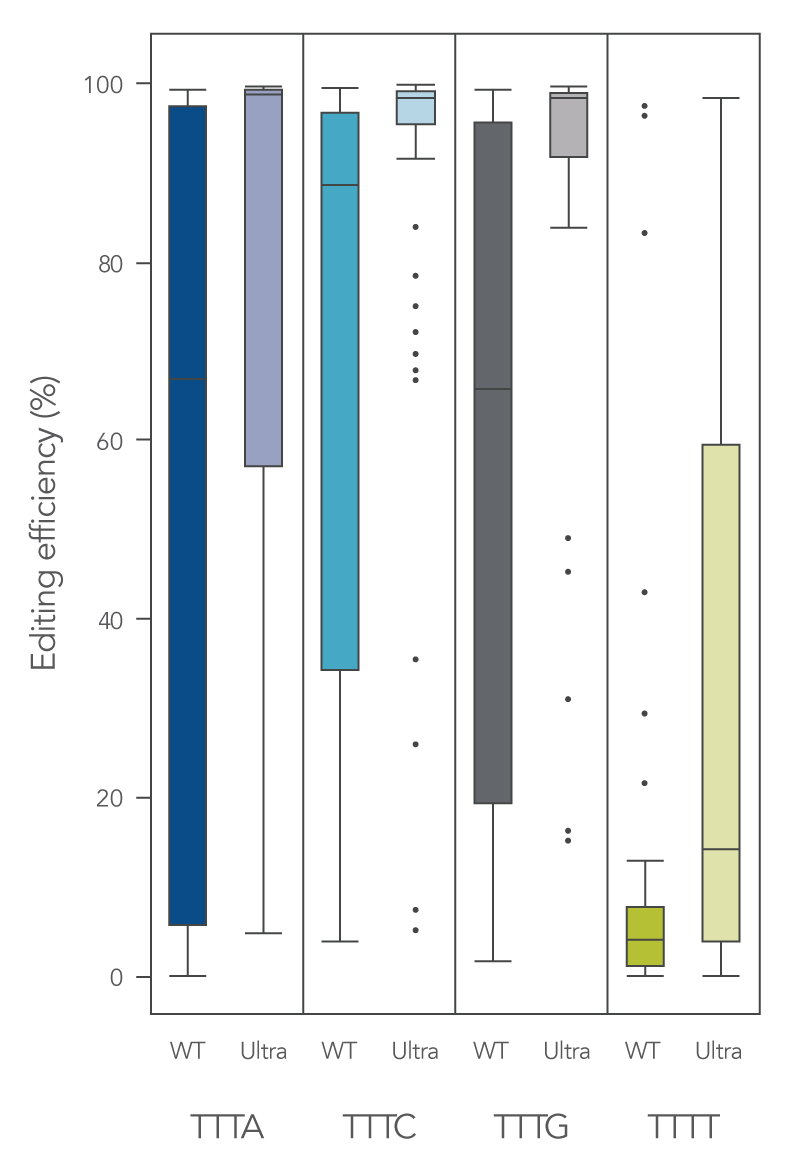
Newly developed Alt-R Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra enzyme increases overall editing efficiency
To enhance activity, we introduced multiple modifications to the Cas12a protein that support notable improvement in overall editing efficiency. The new Alt-R Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra nuclease has higher on-target potency than the wild-type A.s. Cas12a (Cpf1). The new Alt-R Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra also can recognize many TTTT PAM sites in addition to TTTV motifs, increasing target range for genome editing studies (Figure 6). Furthermore, the new Alt-R Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra nuclease is active at room temperature, making it a flexible tool for applications requiring delivery at lower temperatures.
Figure 6. New A.s. Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra exhibits increased genomic editing efficiency in Jurkat and HEK-293 cells. Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes were formed with wild type (WT) or Alt-R A.s. Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra (Ultra), combined with crRNAs synthesized for 120 genomic loci to be delivered in Jurkat cells and 96 genomic loci to be delivered in HEK-293 cells. RNP complexes (4 μM) were delivered into Jurkat and HEK-293 cells via a Nucleofector™ system (Lonza) in the presence of Alt-R Cas12a (Cpf1) Electroporation Enhancer. Genome editing efficiencies were determined by target amplification followed by next generation sequencing on an Illumina instrument. The Cas12a-associated PAM sequences are indicated below the graph. n = 426, with 213 data points for WT and 213 data points for Cas12a Ultra. Each dot represents a single sample.
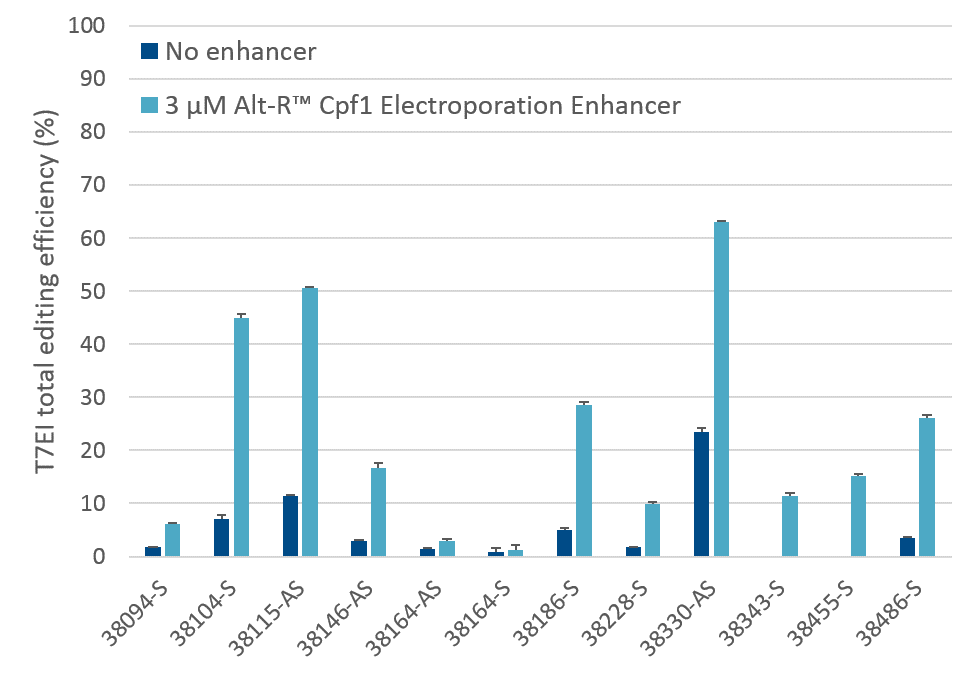
The electroporation enhancer is recommended for efficient genome editing with the CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) system
Figure 7. Alt-R Cas12a (Cpf1) Electroporation Enhancer is required for efficient CRISPR editing in ribonucleoprotein (RNP) electroporation experiments. HEK-293 cells were electroporated with 5 µM RNP (Alt-R A.s. Cpf1 Nuclease 2 NLS complexed with Alt-R CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) crRNA) as instructed in the Alt-R CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) User Guide—RNP electroporation, Nucleofector™ system (available at www.idtdna.com/CRISPR-Cpf1). Twelve Cas12a PAM sites in the HPRT gene were targeted by Alt-R CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) crRNAs. The electroporation reactions contained either no (dark blue) or 3 µM (light blue) Alt-R Cas12a (Cpf1) Electroporation Enhancer. Editing efficiency (n =3) was determined 48 hr after electroporation using the Alt-R Genome Editing Detection Kit, which provides the major components required for T7EI endonuclease assays. PAM = protospacer adjacent motif (Cas12a PAM sequence is TTTV); x-axis: numbers specify gene locations; S = sense strand; AS = antisense strand.
Resources
Frequently asked questions
CRISPR genome editing efficiency seems low - any steps to improve this?
In addition, not every sequence associated with a PAM site performs the same. For example, polymorphisms in the protospacer binding site may reduce editing efficiency. Base mismatches also become more detrimental to editing the closer they are to the PAM site.
We recommend that you try 2 or 3 different PAM sites in your gene of interest to identify a site that provides optimal editing efficiency. Also, be sure to include control experiments. Alt-R™ CRISPR-Cas9 HPRT Positive Controls and Alt-R™ CRISPR-Cas9 Negative Controls are available for human, mouse, and rat.
Please feel free to contact us if you need additional assistance; having the results of your control experiments available will facilitate our ability to help you. For more information, go to www.idtdna.com/ContactUs.
What is the difference between A.s. and L.b. Cas12a? When should I use one or the other?
A.s. Cas12a is from Acidaminococcus sp. BV3L6, and L.b. Cas12a is from Lachnospiraceae bacterium. Both utilize the same TTTV PAM site and crRNA design considerations.
Both Cas12a nucleases result in robust editing at target sites at 37°C, with L.b. Cas12a also resulting in high editing efficiencies in plant genomes and at lower temperatures, such as 23°C.
What CRISPR nucleases are available from IDT?
We are rapidly expanding our offerings—please check back regularly for additional options.
Optimal length for left & right homology arms for CRISPR?
DNA with homology to the sequences flanking a double-stranded break (DSB) can serve as template for error-free homology directed-repair (HDR) of the DSB. The efficiency of HDR is determined by the concentration of donor DNA present at the time of repair, length of the homology arms, cell cycle, and activity of the endogenous repair systems in the particular cell [1]. These factors contribute to the high variability of HDR efficiency observed across different cell lines, and particularly in immortalized cells [2]. Typically, in replicating mammalian cells, donor arms are at least 500 bp in length [3]. However, it is important to determine the optimal HDR conditions for your cell line.
Inserts between the homology arms are frequently in the 1–2 kb range [4]. While longer inserts are possible, the efficiency of recombination decreases as the insert size increases [5]. Finding successfully integrated inserts is likely to be challenging when inserts are greater than 3 kb in most mammalian cells.
Single-stranded oligo DNA (ssODN) has recently been identified as a substrate that is preferred by the HDR mechanism and often achieves good efficiency with homology arms as short as 40 bp [6,7]. The drawback to using ssODNs is that they are limited in length to a few hundred bases, so the insert size is limited. When using Alt-R HDR Donor Oligos as templates for a short insertion, tag, or SNP conversion, we have found arm lengths of 30–60 nt to be sufficient. Modified, linear double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) can also be used as a donor template. For longer, modified dsDNA donors (Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks), we have found homology arm lengths of 200–300 bp to be sufficient for HDR.
For HDR designs, refer to our HDR Design Tool which incorporates these recommendations.
References
- Elliott B, Richardson C, Winderbaum J, et al. Gene conversion tracts from double-strand break repair in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1998; 18(1):93–101.
- Lin S, Staahl BT, Alla RK, et al. Enhanced homology-directed human genome engineering by controlled timing of CRISPR/Cas9 delivery. Elife. 2014;3:e04766.
- Thomas KR, Folger KR, Capecchi MR High frequency targeting of genes to specific sites in the mammalian genome. Cell. 1986;44(3):419–428.
- Dickinson DJ, Ward JD, Reiner DJ, et al. Engineering the Caenorhabditis elegans genome using Cas9-triggered homologous recombination. Nat Methods. 2013;10(10):1028–1034.
- Li K, Wang G, Anderson T, et al. Optimization of genome engineering approaches with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. PloS One. 2014;9(8):e105779.
- Chen F, Pruett-Miller SM, Huang Y, et al. High-frequency genome editing using ssDNA oligonucleotides with zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Methods, 2011;8(9):753–755.
- Davis L, Maizels N. Homology-directed repair of DNA nicks via pathways distinct from canonical double-strand break repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111(10):E924–932.
When using the Alt-R™ S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3, do I follow the same protocols for the standard Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3?
Yes. The Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3 can be directly substituted for the standard Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 in the protocols.
When using the Alt-R™ Cas9 nickases, do I follow the same protocol as the standard Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3?
Yes. The delivery of the CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes with Alt-R Cas9 nickases is similar to RNP with the standard Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3, so the same protocol can be used with these enzymes. However, with the Cas9 nickases, two guide RNAs are required to generate a double-strand break, while only one guide RNA is required for the standard nuclease.
When preparing materials to deliver two guide RNAs simultaneously, first prepare RNPs with each guide RNA separately before RNP delivery.
What reagents will I need in addition to the Alt-R™ RNAs for a CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) genome editing experiment?
The Alt-R™ CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) System includes a target-specific CRISPR-Cas12a crRNA, Cas12a (Cpf1) endonucleases (Alt-R A.s.‑ Cas12a (Cpf1) V3, Alt-R A.s. Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra, or Alt-R L.b. Cas12a (Cpf1) Ultra), and carrier DNA (Alt-R Cpf1 Electroporation Enhancer).
You will need to supply your own electroporation reagents to effectively deliver CRISPR reagents into your cell lines.
We recommend delivery of these reagents as a ribonucleoprotein (RNP). However, Alt-R A.s. Cas12a crRNA also works well in cells that stably express Acidaminococcus sp. BV3L6 Cpf1 nuclease.
We also highly recommend the use of control crRNAs. Control sequences for the CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) system are provided online and in the user guides accessible here.
What methods can be used to deliver the Cas12a ribonucleoprotein (RNP)?
We have successfully used electroporation in internal experiments to deliver Cas12a RNP complexes to cells in culture. In many cell lines, Alt-R™ Cas12a Electroporation Enhancer, a non-targeting carrier DNA, is also required for efficient delivery of the RNP complex. IDT protocols using Cas12a and electroporation are included here, and these Cas12a DECODED articles include functional data and details:
What is the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence for Cas12a (Cpf1)? How is this different from Cas9?
The PAM sequence for the Cas12a (Cpf1) system is TTTV [1], where "V" is a A, C, or G. The Cas12a PAM sequence can be advantageous when working with T-rich target sequences. In contrast, the Cas9 PAM sequence is NGG.
Reference
- Zetsche B, Gootenberg JS, Abudayyeh OO, et al. Cpf1 is a single RNA-guided endonuclease of a class 2 CRISPR-Cas system. Cell. 2015;163(3):759-771.
What is the on-target efficiency of the Alt-R™ S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3?
The on-target efficiency ofAlt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3 is typically 90–100% of the standard Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 efficiency at a specific target site.
The efficiency of both nucleases varies based upon the target site, cell type, and experimental conditions.
What is the expected reduction in off-target effects (OTEs), when using Alt-R™ S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3?
In many cases, Alt-R S.p. HiFi Cas9 Nuclease V3 exhibits a 10–20 fold reduction in editing at problematic off-target sites, when compared with the standard Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3.
The amount of reduction in off-target editing is highly variable and can differ based on multiple factors, including off-target site, ribonucleoprotein (RNP) dose, and cell type.
What is the concentration of the Alt-R™ Cas9 nucleases and nickases?
The Alt-R Cas9 nucleases and nickases are supplied at concentration of 10 mg/mL in 25 mM Tris-Cl, 300 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 50% glycerol (v/v), pH 7.4, with the exception of the Alt-R™ S.p. Cas9 V3, glycerol-free. The Alt-R™ S.p. Cas9 V3, glycerol-free is provided at a concentration of 10 mg/mL in a proprietary buffer without glycerol.
What is the average frequency of the CRISPR-Cas9 PAM sequence in the mammalian genome?
Using the frequency of “GG” = 5.21% in the reference human genome [1], there is an expected 161,284,793 NGG PAM sites in the human genome, or approximately one “GG” dinucleotide every 42 bases.
Reference
- Scherer S. A short guide to the human genome. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2008.
What CRISPR-Cpf1 crRNA controls should I use?
We have recommended positive and negative control sequences for Cpf1 crRNAs available for ordering on the website.
These recommended sequences can be found in the Alt-R® CRISPR Cpf1 user guides (accessible at www.idtdna.com/CRISPR-Cpf1, Support section), and are also available on the side bar of the CRISPR-Cpf1 crRNA ordering pages (accessible at www.idtdna.com/CRISPR-Cpf1).
What buffer should I use to resuspend the Cas12a protein?
All Cas12a variants are provided as a 10 mg/mL solution and, therefore, resuspension is not required.
What buffer should I use to resuspend the Cas9 protein?
All Alt-R™ Cas9 nucleases and nickases are provided in solution at 10 mg/mL, so resuspension is not necessary.
Should I use the Alt-R™ Cas9 D10A or H840A nickase?
It depends upon the experimental design. Cas9 D10A will cut the target strand of DNA (which does not contain the PAM sequence), while Cas9 H840A will cut the non-target strand (which contains the PAM sequence). The availability and location of PAM sites within the target region of DNA needs to be assessed.
Is the PAM sequence part of the CRISPR-Cas9 crRNA construct?
No. The PAM sequence is located on the non-complementary strand. That is, it is on the strand of DNA that contains the same DNA sequence as the target crRNA [1]. The PAM sequence should not be included in the design of the crRNA.
The most commonly used Cas9 nuclease, derived from S. pyogenes, recognizes a PAM sequence of NGG that is found directly downstream of the target sequence in the genomic DNA, on the non-target strand.
Want to Learn More?
Download The CRISPR Basics Handbook that covers applications of CRISPR technology from guide RNA design to data analysis.
The latest CRISPR abbreviations and definitions in a single list!
Design custom solutions for CRISPR genome editing.
Reference
- Anders C, Niewoehner O, et al. (2014) Structural basis of PAM-dependent target DNA recognition by the Cas9 endonuclease. Nature. 513(7519):569–573.
Is the Alt-R™ CRISPR-Cas12a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex stable? Do I need to make a fresh complex for each experiment?
Stability studies for the Alt-R Cas12a RNP complex have found that the Cas12a RNP complex is stable for up to 2 months at 4°C and for up to 1 year at –20°C.
Additional details are included in our CRISPR reagents stability DECODED article.