The Alt-R™ CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) genome editing system
Overview
The combination of Cas12a plus guide RNA forms a ribonucleoprotein (RNP). The RNP cleaves the naturally occurring viral DNA as part of a bacterial immune system. In CRISPR genome editing, scientists can use Cas12a RNP to cut a targeted site in any genome. Alt-R Cas12a Ultra provides high-potency genome editing compared to wild-type Cas12a protein.
CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) genome editing
CRISPR genome editing provides a fast, efficient method of altering the genome of living cells and organisms. The term CRISPR derives from "clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats," which are naturally occurring DNA sequences in prokaryotes. Together with CRISPR-associated (Cas) nucleases these sequences form the basis of a bacterial defense mechanism against viruses. The Cas12a system was first published in 2015 and includes a Cas nuclease capable of creating a double-strand break (DSB) at specifically-targeted sites within the genome [1]. Cas12a is an endonuclease found in many bacterial species, but not all are active in mammalian cells [1]. IDT supports Cas12a enzymes that are derived from Acidaminococcus sp. and Lachnospiraceae bacterium. In genome editing, Cas12a creates a DSB with a staggered 5′ overhang (in contrast to the widely used Cas9, which creates a DSB with blunt ends).
The CRISPR basics handbook
Everything you need to know about CRISPR, from A to Z, from theory to practice, for beginners as well as advanced users.
How CRISPR-Cas12a works
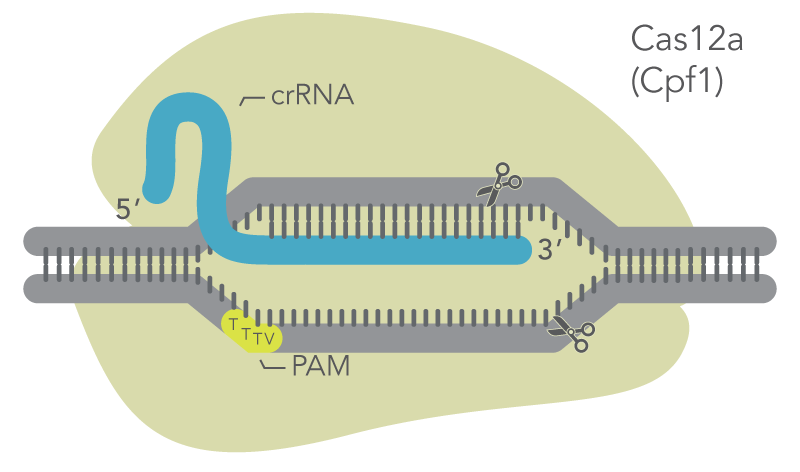
Cas12a is guided to the target site by a short RNA sequence called a CRISPR RNA (crRNA) that is complementary to the target DNA. Cas12a requires only a crRNA to specify the DNA target sequence. Unlike Cas9, no tracrRNA is needed. The target sequence comprises approximately 21 nucleotides and is adjacent to a protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) sequence. The Cas12a enzyme recognizes a unique PAM sequence of TTTV (where V is A, C, or G). Cas12a cuts the strand which contains the PAM at a location 18–19 bases from the 3′ end of the PAM. The cut on the opposite strand of the DNA is 23 bases from the PAM, resulting in a 5′ overhang of 4–5 bases.
When to use CRISPR-Cas12a
The TTTV PAM sequence greatly expands the number of possible editing sites beyond those targeted by Cas9, which requires an NGG PAM site. As a result, Cas12a systems can be used for genome editing in organisms with AT-rich genomes, including model organisms such as plants and C. elegans. Cas12a RNPs can be delivered to a wide variety of cell types using several different methodologies.
IDT has developed a variant of Cas12a which works well at low temperatures and provides similar editing efficiencies as Cas9 at 37°C. This mutant is available as both Alt-R A.s. Cas12a Ultra nuclease and Alt-R L.b. Cas12a Ultra nuclease variants. It has high activity and increases Cas12a editing efficiency. Therefore, Alt-R A.s. or L.b. Cas12a Ultra nucleases are solutions for animal and plant systems whenever a TTTV PAM site is present on either strand of the target genomic DNA. In addition to recognizing standard TTTV PAM sites (i.e., TTTA, TTTG, and TTTC), Cas12a Ultra sometimes is also able to recognize PAM sites with TTTT sequences. At many sites, Cas12a Ultra can recognize “TTTN” PAM sites, where N represents T, A, G, or C (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Cas12a mechanism. Schematic shows Cas12a (Cpf1) with a bound crRNA targeting a genomic site. Cas12a creates a double-strand cut with staggered ends. The TTTV PAM site is on the strand opposite to the targeted strand. Alt-R Cas12a Ultra has the same mechanism as wild-type Cas12a while displaying greater potency and higher tolerance for a wider range of temperatures than wild type.
Products for CRISPR-Cas12a genome editing
References
- Zetsche B, Gootenberg JS, Abudayyeh OO, et al. Cpf1 is a single RNA-guided endonuclease of a class 2 CRISPR-Cas system. Cell. 2015;163(3):759-771.