The IDT Codon Optimization Tool simplifies designing synthetic genes and single-stranded or double-stranded DNA fragments for expression in a variety of organisms. The main design consideration is to optimize a DNA or protein sequence from one host organism for expression in another by re‑assigning codon usage.
The tool also makes it easy to adjust a sequence that has difficult secondary structure, a repetitive motif, or high/low GC content for compatibility with IDT manufacturing requirements for single-stranded and double-stranded gene fragments.
Easy steps for use
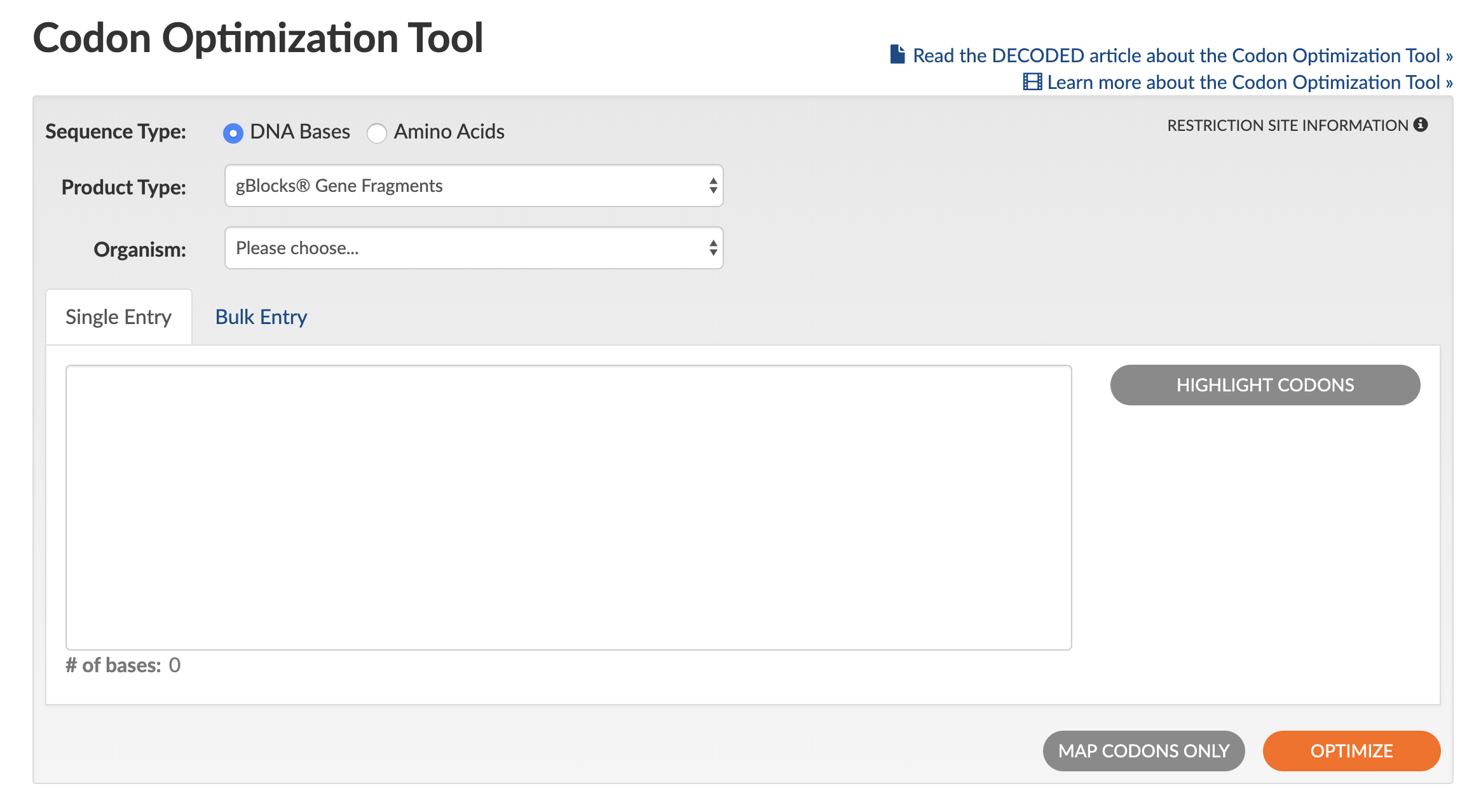
Use of the Codon Optimization Tool is straightforward (see Figure 1 for a screen shot of the tool interface):
- Select the Sequence Type by clicking either DNA Bases or Amino Acids.
- Select the desired Product Type of either gBlocks™ Gene Fragments, Gene, Megamer™ ssDNA Fragments, eBlocks™ Gene Fragments,or gBlocks HiFi Gene Fragments to set the optimization rules that the tool will use.
- Select your Organism for expression from the pulldown list (if working with cell lines, select animal or plant origin).
- Paste in your sequence (bulk entry is also available in a variety of input formats).
- (Optional) To designate a specific part of the sequence for optimization, click on Highlight Codons. You can then edit the sequence by changing the reading frame shift and by indicating start/stop codons.
- Obtain results in one of the following ways:
- Use default optimization rules
- Click on Optimize (lower right orange button).
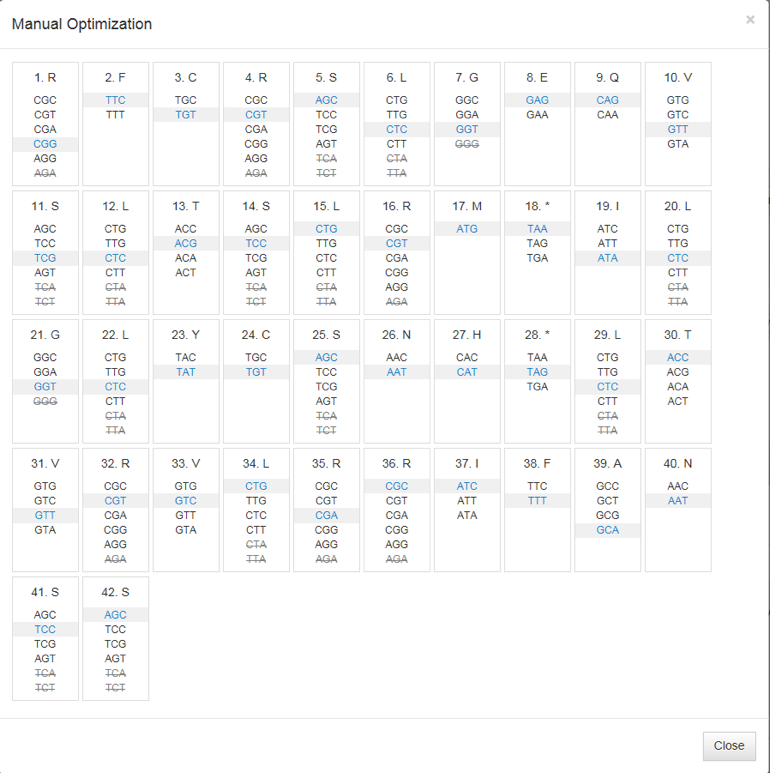
Note: multiple clicks on the Optimize button will generate slightly different sequences. - (Optional; available only for amino acid sequences) Click on Manual Optimization (Figure 2) to change codon usage for any amino acid or stop codon in your sequence (Figure 3).
- Click on Optimize (lower right orange button).
- To manually optimize your original sequence, click on Map Codons Only and then Manual Optimization (Figure 2) to change codon usage for any amino acid or stop codon in your sequence (Figure 3).
- Use default optimization rules
- Order sequence using the blue Order item button.
Natural codon bias and optimized sequence ranking
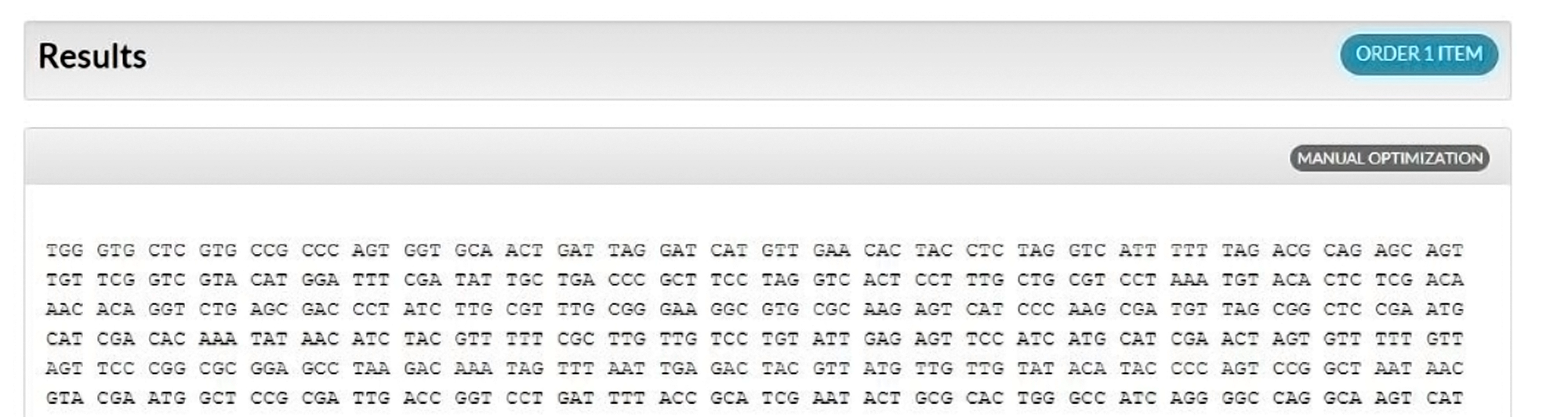
The Codon Optimization Tool randomly chooses codons with a bias similar to the natural bias observed in the selected organism’s genome (Figure 2); however, rare codons present less than 10% of the time are not included (for example, Figure 3, codon 1, AGA). With no one-to-one codon to amino acid assignment by the algorithm, multiple optimization attempts of the same sequence will generate different results, possibly having different restriction enzyme sites, as synonymous codons are assigned based on frequencies found in the selected codon table.
With the Manual Optimization view (Figure 3), you can make desired changes to individual codons by simply clicking on their locations. Hovering your cursor over a particular codon will generate a pop out window showing codon frequency. Changes made using Manual Optimization are automatically reflected in the results.
A caveat: Does codon optimization equal higher expression?
While codon optimization is important for optimal protein expression, it does not guarantee higher expression levels. Additional factors, such as mRNA stability, protein maturation, translation speed, chaperone expression, promoter design, etc. also influence expression.
Get started
Instead of spending days designing and constructing your synthetic gene, use the Codon Optimization Tool to order your gene in minutes through IDT and spend the saved time advancing your research while we make your genes or gene fragments.
Access IDT’s free online Codon Optimization Tool and get started.
We also provide a step-by-step video tutorial for using the Codon Optimization Tool.
Contact us
If you are working with an organism not listed in the Codon Optimization Tool’s Organism list, or do not see the information you need, contact us. We can accept non-standard optimizations that fall outside of the rules used by the tool (design fee may apply).
*RUO—For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Unless otherwise agreed to in writing, IDT does not intend for these products to be used in clinical applications and does not warrant their fitness or suitability
for any clinical diagnostic use. Purchaser is solely responsible for all decisions regarding the use of these products and any associated regulatory or legal obligations. Doc ID: RUO23-1936_001